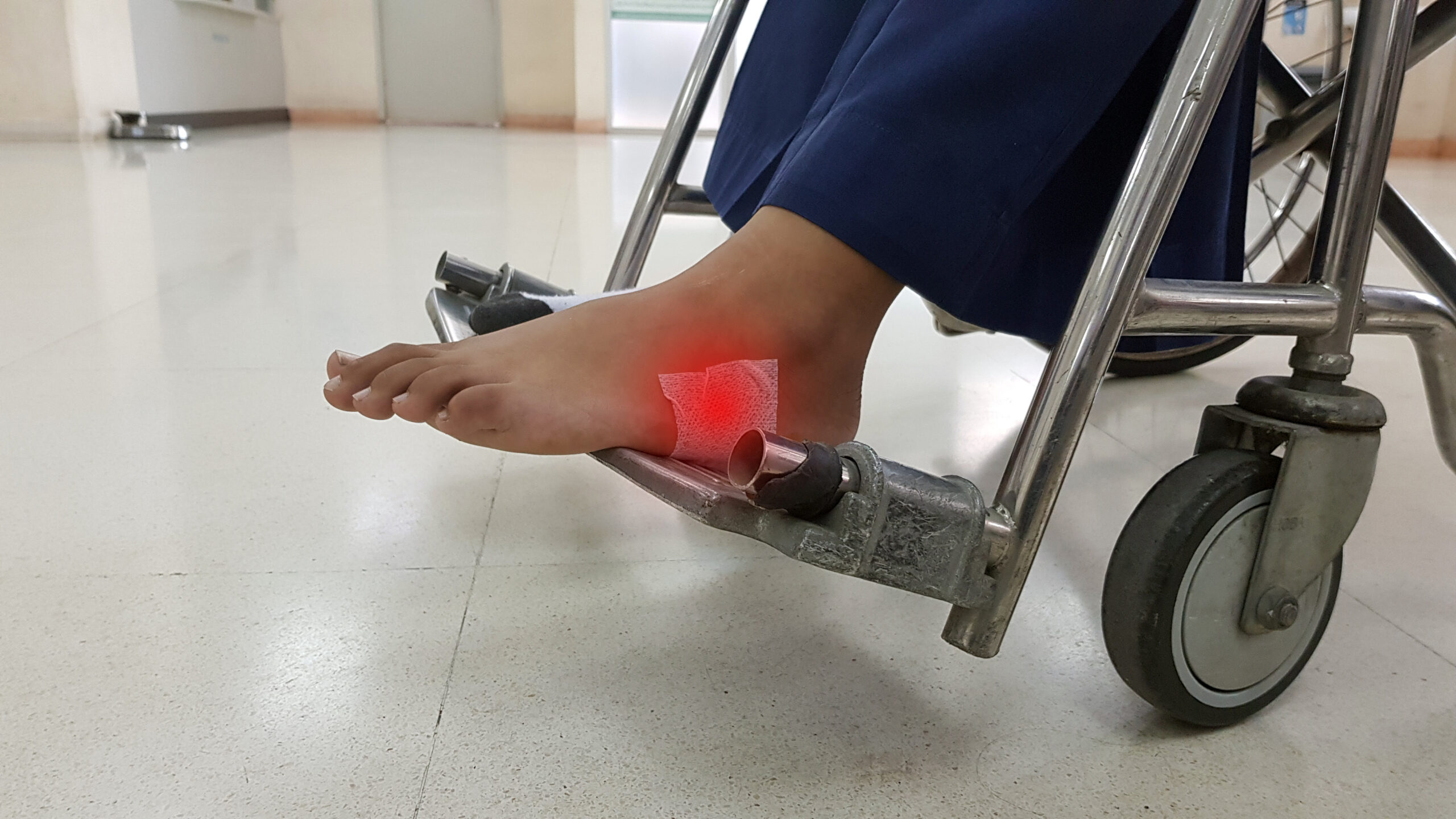
Diabetics are more susceptible to certain conditions, and with that, they are more likely to develop different types of wounds on their feet and ankles. These diabetic wounds can occur for different reasons such as poor circulation and nerve damage. If they are not addressed they can lead to infection and other severe complications. However, with proper foot care and assistance from a podiatrist, diabetic wounds can be monitored or even prevented.
The primary causes of diabetic wounds on the foot or ankle are poor circulation and nerve damage, also known as neuropathy. Diabetics develop poor circulation as the inability to process glucose correctly leads to high levels in the body. In turn, fatty deposits form in the blood vessels that harden and narrow them over time, leading to poor circulation (UCLA, 2021). Neuropathy happens as increased levels of glucose and fat in the blood cause damage to the nerves. To learn more about these conditions such as their causes, symptoms, and treatments, visit our blog posts titled “Diabetes and Foot Problems” and “What is Diabetic Neuropathy?”.
Poor circulation and neuropathy both impair sensation in the feet, allowing wounds to go unnoticed (Cleveland Clinic, 2022). The healing process can also be significantly slower as the supply of necessary nutrients in the area can decrease due to poor circulation. Undiscovered wounds that do not heal properly can lead to serious problems.
Diabetic wounds can develop anywhere on the foot or ankle but are especially common in areas that experience prolonged pressure. Wounds in their early stages can appear to just be skin that is dry, red, cracked, or scaly. While it can be easy to brush those signs off, it is extremely important for diabetics to monitor all changes. Something that seems harmless can continue to develop into a very dangerous issue. Signs of wound progression include further discoloration, calluses in the area, and odor or drainage in the area which can indicate infection (Cleveland Clinic, 2022). Treatment varies depending on the extent of the wound. Early wounds might be treatable with creams, antibiotics, or compression. However, more severe wounds can require surgeries to remove the infected areas of skin, scar tissue, or bone, and can even lead to amputation.
As these wounds are so common for diabetics, the best way to prevent them is to closely monitor their feet for any changes. Taking the time each day to look for any cuts, sores, blisters, redness, or anything out of the ordinary, is essential. The earlier wounds are discovered, the more likely that they will require less invasive treatment. Additionally, monitoring glucose levels closely and wearing proper footwear can help prevent wounds from developing (University of Michigan, 2022). It is highly recommended that diabetics visit podiatrists regularly.
If you are diabetic and believe you might be developing a wound or ulcer, give us a call. We are here to answer questions and address any concerns you may have. Alternatively, if you are diabetic and looking for a podiatric office in order to learn about foot care and wound prevention, contact us today to schedule a new patient appointment. Our experienced team specializes in diabetic foot care and takes pride in providing high-quality care.