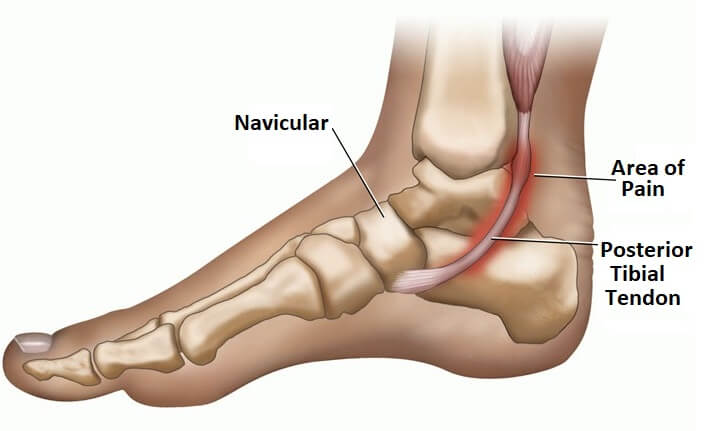
The posterior tibial tendon is considered one of the most important tendons in the leg. This tendon attaches the calf muscle to the bones on the inside of the foot. Its main purpose is to support the foot and hold up the arch when walking.
Posterior Tibial Tendonitis is a very common problem in the foot and the ankle and occurs when the tendon becomes torn or inflamed. As a result of one of these two issues, there is a lack of support and stability which could cause flatfoot. This can cause additional pain in the foot, particularly in the heel or arch area.
There are a few things that could cause a tear or inflammation in the posterior tibial tendon. These can include a fall and overuse of the tendon such as participating in high- activity sports on a consistent basis. The tendon will slowly collapse over time and can cause flatfoot.
There are a number of symptoms that can be a sign of Posterior Tibial Tendonitis. You may have pain along the inside of the foot and ankle which can be associated with swelling. If you run often, this pain will be noticeably worse and can be difficult to walk or stand. There can also be pain on the outside of the foot. When the foot collapses this can cause the heel bone to shift to a new outward position. This puts pressure on the outside of the ankle.
There are a variety of treatments for Posterior Tibial Tendonitis, depending on the severity of the issue. There are non-surgical treatments such as rest, ice, anti- inflammatory medication, physical therapy and braces. If the tendonitis is more serious, there are multiple surgical options that would correct the issue. This is determined by the surgeon.
If you have any of these symptoms or feel that you may have Posterior Tibial Tendonitis, contact a physician today.
